What is Laparoscopic Gastric Sleeve resection?
It is a bariatric procedure in which the outer crescent of the stomach is removed, and the stomach’s ability to hold food is severely reduced at the end of the procedure, leaving behind a tube-like stomach. As a result of the stomach’s reduced capacity to hold food, people’s ability to swallow food declines, resulting in weight loss over time.
How is the procedure performed?
A Laparoscope (a tiny instrument with a thin tube and camera at the end) and other equipment are inserted into 5 to 6 small incisions to do the process.
The procedure comprises removing 2/3 of the stomach on the left side using laparoscopic methods and endoscopic staplers. As a result, the stomach takes on a tube-like form (similar to a hockey stick), restricting the stomach’s capacity to store food. The entire process is carried out after the patient has been given anesthesia, and because he is unconscious during the procedure, he experiences no discomfort.
Who should opt for this procedure and
why is it performed?
People who eat a lot of food, are 30 kg overweight, have a BMI of more than 32, and suffer from co-morbidities.
What are the benefits of going through with the procedure?
The
following are some
of the procedure’s advantages:
-A 60-70 percent weight loss is assured.
– The ability to manage related co-morbidities improves.
– This is an option for those who aren’t eligible for malabsorptive or other
combination therapies.
How does this procedure aid in
weight loss?
This is a restrictive surgery that substantially reduces the size of the stomach, reducing the stomach’s ability to retain food, leading to a decrease in appetite, and, as a result, the individual consumes less food. The procedure also reduces the release of ghrelin, the “hunger hormone,” which causes a decrease in appetite and, as a result, weight loss. Many studies have shown that the benefits of this strategy may last up to three years and that it can help you lose a lot of weight
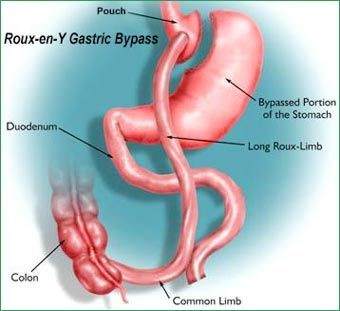
Laparoscopic Gastric Bypass
What is Laparoscopic Gastric Bypass?
How is the procedure performed?
In
laparoscopic gastric bypass surgery, which is considered one of the most
effective weight loss procedures, the surgeon staples the upper section of the
stomach, resulting in a smaller stomach pouch. The smaller stomach pouch
reduces food consumption.
This little stomach pouch is connected to a section of the small intestine
called the jejunum, which allows food to skip the lower stomach. As a result of
this procedure, the amount of calories that the body can absorb is lowered,
which is known as malabsorption. This surgery is also known as a Roux-en-Y
bypass.
What are the benefits of the surgery?
The
following are some of the advantages of the surgery: When compared to
other restrictive therapies, the procedure increases the average pace of weight
loss if you completely follow the instructions.
According to research, a year following surgery, a person’s weight loss
percentage is 77 percent.
According to research, patients retain 50 to 60 percent of their excess weight
loss 10 to 15 years after therapy.
According to research, back discomfort, high blood pressure, and depression
were all alleviated in 96 percent of those who had the operation.
How is the procedure carried out?
5 to 6 small incisions are made, and a Laparoscope (a narrow tube with a camera at the end) is inserted through those incisions. Once the surgeon has clear visuals from the Laparoscope, surgical instruments are inserted through other incisions, the top portion of the stomach pouch is stapled, and the section of the smaller stomach pouch is connected to the small intestine, facilitating the malabsorption process. During the procedure, anesthesia is employed.
How long does it take to recover?
Laparoscopic
surgery has a far shorter recovery period than open surgery.
After spending 2–3 days in the hospital, it will take 3–5 weeks to return to
normal activities.
The doctor may prescribe blood tests and other tests to assess the patient’s
health during the first few weeks following recovery.
When it comes to eating, the patient must follow a specific diet that involves
a transition from fluids to pureed meals. Following that, the patient can start
eating softer meals and gradually build up their tolerance to more traditional
foods.
Multivitamin and multimineral pills will be prescribed by doctors to aid
healing by filling up laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding
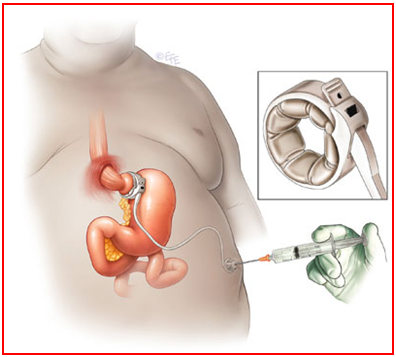
What is Laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding?
The laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding (LAGB) procedure is a type of bariatric surgery. It’s performed in the same way as other Laparoscopic surgeries, using small incisions. The surgeon wraps a small adjustable band around the top of the stomach, causing the stomach pouch to shrink and resulting in less food consumption and weight loss.
Who needs Laparoscopically adjustable gastric banding surgery?
This operation is required for those who have obesity difficulties, abnormal weight gain, or a BMI of more than 40.
How is the procedure carried out and how should one prepare for it?
The
procedure takes 30 to 60 minutes to complete and is performed under anesthesia.
The surgeon makes tiny incisions in the upper abdomen and inserts a Laparoscope
(a little tube with a camera at the end) to examine the stomach. Through the
incisions, more surgical equipment is inserted, and an adjustable band is
wrapped around the upper stomach pouch.
The doctor will advise the patient to cease taking any extra medications, such
as blood thinners or diabetic medications, before surgery. If the patient
smokes or consumes tobacco in any other form, it is suggested that he or she
stops since tobacco consumption slows healing following surgery.
how long does it take and what are the benefits?
· The recuperation period is reduced due to the few incisions created during the treatment.
If all of the patient’s vital signs are normal, he may be dismissed the same
day.
According to studies, the participants lose up to 40 percent to 50 percent of
their extra weight after surgery.
Because the operation is reversible, there is no disruption to natural anatomy.
When compared to an open treatment, the discomfort of surgical wounds after
surgery is less, and recuperation is very swift.
The patient can resume normal activities in 2 to 3 weeks.
During the initial few weeks after recuperation, the doctor may urge the
patient to have blood work and different tests are done to check their health.
· In terms of eating, the patient must first adhere to a particular diet, which includes a transition from liquid to pureed foods. After that, the patient can begin eating softer foods and gradually progress to typical foods as their tolerance improves.
Doctors will prescribe multivitamin and multi-mineral tablets to help bridge
the nutritional deficit and boost recuperation during the healing process.
Iron, calcium, and vitamin B12 may be among the vitamins and minerals given.
Patients will make good progress.
traditional deficits. Among the nutrients are
iron, calcium, and vitamin B12

